Underwater Metal Detectors: Ultimate Guide For Treasure Hunter Diving
Ever wondered what mysteries lie beneath the ocean floor, waiting to be uncovered? For avid scuba divers seeking an added dimension of thrill and adventure, the answer might just be hidden treasures waiting to be discovered with underwater metal detectors.
In this comprehensive guide, I will delve into the realm of underwater metal detectors—a tool that not only unlocks the potential for uncovering submerged artifacts but also elevates your diving experience.
From understanding their critical features to finding the best detector for your diving needs, this guide will help you get started. Already own an underwater metal detector? Read on to learn how to safely get the best performance out of your detecting equipment.
What is an underwater metal detector?
An underwater metal detector is a specialized device designed to detect metallic objects submerged beneath the sea floor. They can play a crucial role in various diving activities, including wreck discovery, underwater archeology, treasure hunting, and search and recovery.
These detectors are waterproof and built to withstand the conditions of aquatic environments, allowing divers and enthusiasts to locate metal objects such as jewelry, artifacts, or other submerged treasures.
Underwater metal detectors operate on different technologies, including Pulse Induction (PI) and Very Low-Frequency (VLF), each with its advantages and applications. They provide visual, audible, or vibration alerts to signal the presence of metal underwater, enhancing the user’s ability to explore and discover objects hidden beneath the ocean floor.
Why do scuba divers use underwater metal detectors?
Scuba divers use underwater metal detectors for several reasons:
- Treasure Hunting and Exploration: Underwater metal detectors allow divers to search for hidden treasures and artifacts beneath the ocean floor, turning their dives into exciting treasure hunts.
- Locating Lost Items: Divers use these detectors to find lost items like jewelry, cameras, or other valuables that may have slipped from their grasp during a dive.
- Historical and Archaeological Exploration: Underwater metal detectors are crucial tools for underwater archaeologists and historians, helping them discover and document historical shipwrecks and artifacts.
- Environmental Cleanup: Some divers use metal detectors to contribute to environmental conservation by collecting and removing metallic debris from the underwater environment.
- Safety: Detecting submerged metal objects can enhance diver safety by helping avoid potential hazards, such as sharp objects or entanglements.
How To Use Underwater Metal Detectors For Marine Archaeology
Types of Underwater Metal Detectors
There are two main types of underwater metal detectors, each utilizing distinct technologies:
- Pulse Induction (PI) Metal Detectors:
- Technology: PI detectors generate short bursts of electrical current, creating magnetic fields. When the pulse is turned off, the magnetic field collapses, inducing a voltage spike. Metal objects disrupt this process, producing a distinctive signal.
- Advantages: Excellent depth penetration, making them ideal for deep-ground and highly mineralized soil conditions.
- Drawbacks: Limited discrimination capabilities, making it challenging to differentiate between types of metals.
- Very Low-Frequency (VLF) Metal Detectors:
- Technology: VLF detectors operate by transmitting and receiving continuous low-frequency signals. Changes in the magnetic field caused by metallic objects generate audio signals.
- Advantages: Better discrimination capabilities, allowing users to identify specific metals. Suitable for various underwater environments.
- Drawbacks: Reduced depth performance compared to PI detectors.
Pulse Induction Metal Detectors ($-$$)
Pulse Induction underwater metal detectors are ideal for less experienced divers and those who just want to do some quick detecting during their dives. They usually have simple ‘turn on and start‘ controls, lacking complex displays for a quick start.
PI underwater metal detectors effectively cancel out minerals like salt and black sand, allowing deeper-range detection. While excelling at target pinpointing, their drawback lies in limited discrimination against junk. This may waste valuable dive time on disappointing detections when bottom time is limited.
VLF Underwater Metal Detectors ($$$)
Very Low Frequency (VLF) metal detectors excel at finding coins, relics, and jewelry while discriminating against junk. They often boast advanced displays and audio identification, achieving significant detection depth.
Although sensitive to water mineralization, VLF detectors are versatile and ideal for all-purpose treasure hunting with proper ground balancing.
Multifrequency Metal Detectors ($$$$)
Multifrequency metal detectors, also known as simultaneous multifrequency detectors, utilize advanced technology to operate on multiple frequencies simultaneously.
Unlike single-frequency VLF detectors, multifrequency detectors can transmit and receive signals across a range of frequencies concurrently.
Signal Interference in Underwater Metal Detectors
Mineralization and Saltwater Conductivity
Mineralization and saltwater conductivity are factors that affect underwater metal detector performance.
- Mineralization: In underwater contexts, mineralization refers to the presence of various minerals in the seabed or soil.
- These minerals, such as iron and magnesium, can disrupt the electromagnetic signals emitted by metal detectors.
- It essentially introduces a layer of “background noise” that can interfere with the detector’s ability to discern specific metal signatures.
- Conductive Saltwater: The salts in seawater enhance its conductivity, posing a challenge for metal detectors.
- As your detector emits signals, the conductive nature of saltwater can cause these signals to scatter and distort, affecting the accuracy of the detection process.
In short, highly mineralized environments and saltwater can disrupt electromagnetic signals. When your detector sends out signals to locate metal objects, these minerals and conductive properties can interfere, creating noise and making it challenging to distinguish between the signals emitted by the detector and those bounced back from metal objects.
Metallic Objects and Complex Terrain
Navigating through underwater environments filled with metallic objects and complex terrains presents unique challenges:
- Metallic Objects: The underwater world isn’t just home to the treasures you seek; it’s often littered with other metallic objects, from discarded equipment to natural mineral formations. This abundance of metal can lead to false signals or reduced sensitivity, complicating the task of identifying your target amidst the underwater metallic landscape.
- Complex Terrains: Uneven terrains, such as rocky seabeds or coral reefs, pose challenges for metal detectors. The irregularities in these terrains can impact the detector’s ability to maintain consistent contact with the seabed, affecting its overall performance.
Electromagnetic Field Stability
Now, let’s talk about the stability of the electromagnetic field (EMF). The electromagnetic field is what an underwater metal detector uses to interact with metal objects.
If this field is unstable due to interference, your detector’s accuracy takes a hit. It might struggle to provide precise information about the location and composition of the metal objects.
- EMF Stability: The electromagnetic field generated by your detector is the tool it uses to interact with metal objects. Interference disrupts this field, causing fluctuations in stability. These disruptions directly translate to inaccuracies in detecting the location, size, and composition of metal objects underwater.
Ground Balance Features
Ground balance is the feature on some metal detectors that allows them to ignore EMF signal interference from the ground while still detecting metal objects. It’s like teaching your detector to filter out the noise from mineralized soil and challenging terrains.
- Noise Filtering: Ground balance acts as a sophisticated filter, distinguishing between signals from the ground and those from metal objects. This noise-filtering capability minimizes interference by allowing the detector to focus on genuine metal signals while disregarding signals from the surrounding environment.
- Adaptability: Ground balance adjusts to different soil conditions. Whether you’re diving on a sandy bottom or a highly mineralized rocky terrain, it ensures optimal performance across diverse underwater environments.
Signal Interference: VLF and PI Detectors
Let’s dive into the pros and cons of VLF and PI detectors with respect to signal interference underwater:
- VLF Detectors: These detectors excel in less challenging environments but become susceptible to interference in highly mineralized soils. The minerals create a magnetic “background noise” that can overshadow the signals from your target, potentially leading to missed detections.
- PI Detectors: Pulse Induction detectors showcase a distinct advantage in environments with high mineralization. Their robust design allows them to power through the interference caused by mineralized soils, making them the preferred choice for underwater use in highly mineralized terrains.
Key Features to Consider In An Underwater Metal Detector
Depth Rating
When choosing an underwater metal detector, the depth rating is a critical factor to consider. Select a unit that performs well, and will not flood, at the deepest depth range you plan to dive.
Greater Depth Range: A higher depth rating expands your underwater exploration possibilities, enabling you to delve into deeper waters.
The depth rating indicates the maximum depth at which the detector can operate effectively. A higher depth rating allows you to explore more challenging environments without compromising the detector’s functionality.
Choosing the Right Depth Rating for Your Needs
Consider your typical diving locations and the depths you plan to explore. If you’re primarily diving in shallow waters, a lower depth rating might suffice, saving you on cost and potentially providing a more lightweight option.
However, for those venturing to deeper depths or engaging in technical diving, investing in a detector with a higher depth rating is imperative to ensure accurate and reliable performance at greater depths.
Target Discrimination
Target discrimination is a key feature that determines the detector’s ability to distinguish between different metals. This feature is crucial for avoiding false positives, especially in areas with high metal debris or multiple metal targets.
- Conductivity Analysis: Discrimination settings analyze the conductivity and composition of detected objects.
- Customization: Customize settings based on metal preferences, eliminating signals from undesired metals.
Discrimination settings allow you to focus on valuable targets while ignoring unwanted items, enhancing the efficiency of your underwater treasure hunting.
How Discrimination Settings Work
Adjustable discrimination settings are based on the conductivity and ferrous properties of metals. You can customize the detector to respond differently to various metals, allowing you to filter out common underwater debris while honing in on specific treasures.
Understanding and mastering discrimination settings significantly improves your chances of successful and targeted metal detection during dives.
Detector Size and Weight
The size and weight of an underwater metal detector make a big difference in the success of your dive goals.
- Maneuverability: Compact and lightweight detectors ensure ease of maneuverability when diving.
- Balancing Functionality: Balance between portability and performance to maintain necessary functionality.
Compact and lightweight detectors are typically preferable for casual recreational divers, offering ease of handling and control. A well-balanced and ergonomic design contributes to a comfortable diving experience, reducing fatigue during prolonged use.
On the other hand, more experienced divers engaging in serious metal detecting dives may compromise convenience for a heavier detector with advanced features to maximize detection capabilities.
Prioritize a detector that aligns with your detecting goals, skill proficiency, experience, and the profile of your planned dives.
Best Underwater Metal Detectors
Whilst the best underwater metal detector for you will be determined by budget and a range of individual preferences and needs, here are some ideas:
Fisher Underwater Metal Detectors
Fisher is a highly-regarded manufacturer of underwater metal detectors. The Fisher CZ-21 Quicksilver is their premium multi-frequency detector, waterproof to 67m/250ft.
Garrett Underwater Metal Detectors
Garrett produces a wide range of metal detectors and offers several units suitable for scuba divers. The Sea Hunter Mk2 is my recommendation from their range. It is waterproof to 60m/200ft.
Minelab Underwater Metal Detectors
Minelab is a premium metal detector manufacturer with a reputation for high-quality products. The multi-frequency Excalibur II is their specialized detector for scuba divers, being waterproof to 66m/200ft.
Other Brands of Underwater Metal Detectors
There are a number of economy brands that offer underwater metal detectors. These may be more suitable for beginners, or divers on a limited budget. Always confirm the waterproof depth rating and pay close attention to the features offered.
Search Patterns For Underwater Metal Detecting
Getting the best out of an underwater metal detector involves conducting a calculated search of the sea floor. This can be done by using an underwater search pattern. These patterns are typically taught in Rescue Diver or Search and Recovery courses.
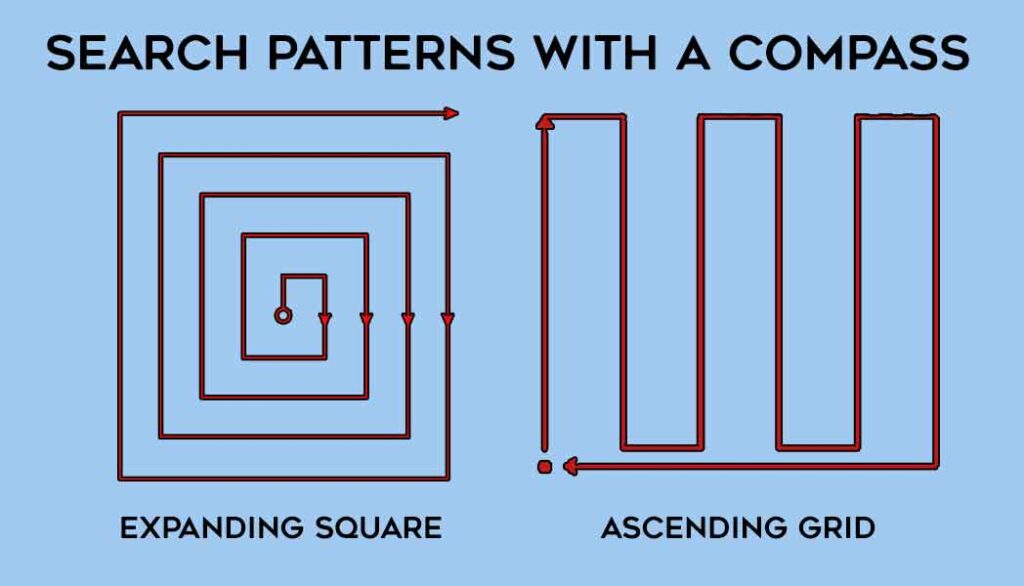
Search Patterns Using a Diving Compass
Some underwater search patterns use an underwater compass to provide navigation. The diver uses the compass to set the appropriate angle, then travels a pre-decided distance before making the next turn.
- Expanding Square Pattern: This popular underwater search pattern involves divers systematically expanding their search area in a square or rectangular pattern. It’s effective for covering large areas and is commonly used in search and recovery operations.
- Ascending Grid Pattern: The diver uses their compass to travel up and down a pre-designated area using parallel lines. This U-shaped pattern is good for quickly covering an area and is less obstructed by objects within the search area.
Search Patterns Using a Diving Reel or Finger Spool
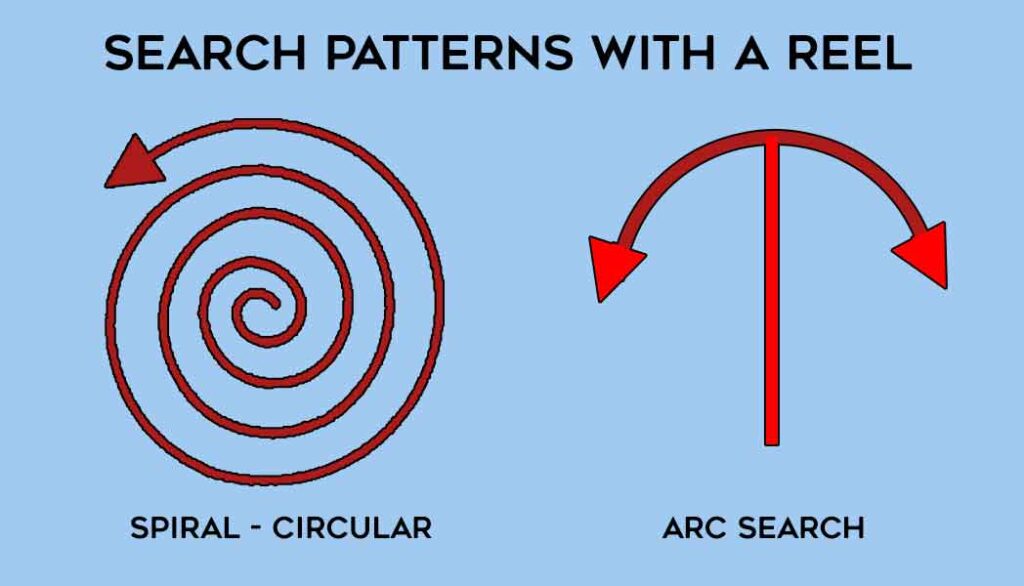
Some search patterns can be managed by using a diving reel or A 30-40m (100-130ft) finger spool. These involve making a tie-off at the central location and searching outwards using a guideline.
They are accurate, less cognitively demanding, and easy to implement. They are best employed when the sea floor is flat and without obstacles or obstructions that can tangle the guideline.
- Arc Search Pattern: A simple yet effective method, the arc search involves divers sweeping back and forth in an arc shape. This pattern is frequently used due to its efficiency in covering a wide area and is a staple in public safety diving.
- Circular/Spiral Search Pattern: This technique involves divers conducting a spiraling circular search around a central point. It’s useful for exploring areas with a distinct center and is part of the repertoire of search and recovery operations.
The Impact of Underwater Metal Detectors on Diver Safety
Consider your diving safety while diving with an underwater metal detector. The following factors should be encompassed within your pre-dive risk management planning:
- Task Loading: Adding more tasks to your dive increases your cognitive load. This causes mental fatigue and prevents you from focusing on other dive skill requirements. In turn, the risk of mistakes and accidents increases.
- Situational Awareness: Using an underwater metal detector involves mental focus. Be aware that fixating on your detector will reduce your awareness of other critical dive information, such as gas supply, depth, bottom time, and your buddy.
- Buoyancy Control: The weight of an underwater metal detector has to be supported by your BCD. This, in turn, will make controlling your buoyancy more difficult, especially on descent and ascent.
- Gas Consumption: Operating a detector can increase the amount of gas that you consume during your dive. Use gas management to calculate your SAC rate when detecting, and apply this during dive planning.
- Bottom Time: There is more chance of exceeding a no-stop (NDL) limit if you are distracted by focusing on your underwater metal detector. Work as a diving team to prevent impaired situational awareness from causing decompression emergencies. Make sure that you have a contingency plan for accidentally exceeding your planned bottom time.
- Emergency Management: An unrelated emergency can still occur when you are metal detecting on a dive. Carrying the detector can impede your ability to respond to emergencies. Consider the realities of these situations when determining your emergency response plans for foreseeable diving risks.
Minimizing Risk When Underwater Metal Detecting
- Environmental Assessment:
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment of the dive site before metal detecting. Identify potential risks such as underwater currents, visibility issues, and hazardous marine life.
- Knowledge of Dive Site:
- Acquire in-depth knowledge of the specific dive site, including potential hazards, to minimize risks associated with underwater metal detecting activities.
- Emergency Preparedness:
- Develop and practice emergency response plans for unforeseen situations. This includes procedures for equipment failure, entanglement, mandatory decompression, gas depletion, medical emergencies, or any other potential risks.
- Communication Protocols:
- Establish clear communication protocols with dive buddies or support teams. Effective communication enhances coordination during metal detecting, minimizing risks associated with miscommunication.
- Regular Breaks and Monitoring:
- Take regular breaks during metal detecting sessions to prevent fatigue and regain situational awareness. Continuous monitoring of air supply, equipment status, and personal well-being is essential for safe underwater activities.
- Adherence to Safe Diving Practices:
- Integrate metal-detecting activities with established dive safety protocols and standards. Adhering to recognized regulations ensures a systematic and safe approach to underwater exploration.
- Skill Proficiency:
- Ensure that your fundamental diving skills are practiced to an ingrained, unconscious, level of performance. This prevents them from degrading when you are task-loaded.
- Practice operating your underwater metal detector on shallower, low consequence, dives before taking it to deeper depths or more challenging dive conditions.
Operating An Underwater Metal Detector Effectively
To make the most out of your underwater metal detector, you need to grasp the signals it gives you. Understanding these signals and tweaking the settings just right is key for optimal performance.
1. Audio Interpretation
When it comes to underwater metal detectors, the language they speak is in tones and patterns. Each metal produces a distinct sound, and understanding this auditory feedback is paramount.
Tips for Audio Interpretation
- Familiarization: Spend time listening to the audio signals in controlled environments. Familiarize yourself with how different metals sound, creating a mental library of these unique tones.
- Regular Practice: Practice makes perfect. Regularly expose yourself to different metal objects and listen to the detector’s response. This hands-on experience hones your ability to accurately distinguish between signals in real-world scenarios.
- Varied Environments: Conduct practice sessions in various underwater environments. Different conditions, such as currents and sediment, can impact the way signals travel. Adapting to these variations improves your overall proficiency.
2. Visual Displays
Some modern underwater metal detectors come equipped with visual displays that provide additional information about detected metals. Understanding these visual cues is a valuable skill for efficient metal identification.
Tips for Visual Display Interpretation
- Study the Manual: Each detector model may have unique visual indicators. Thoroughly study the user manual to understand the specific symbols and readings displayed on your detector.
- Hands-On Learning: Spend time experimenting with the detector in controlled settings. Create scenarios with known metal objects to observe how the visual display responds. This practical approach accelerates your learning curve.
- Night Diving Considerations: If you engage in night diving, understanding how your detector’s display works in low-light conditions is crucial. Familiarize yourself with any backlight features and practice using them.
3. Discrimination Settings
Discrimination settings empower you to filter out unwanted metals, reducing the chances of false positives and focusing on valuable targets. Mastery of these settings is fundamental to optimizing your underwater metal-detecting experience.
Tips for Discrimination Settings
- Metal Profiles: Understand the discrimination profiles on your detector. These profiles are pre-set configurations designed for specific types of metals. Customizing these profiles based on your preferences and the area you’re exploring enhances accuracy.
- Field Testing: Regularly test your discrimination settings in the field. Experiment with different configurations to find the optimal balance between sensitivity and discrimination for the specific environment you’re in.
- Continuous Adjustment: Conditions underwater can change rapidly. Be prepared to adjust your discrimination settings as you move through different areas. Fine-tuning in real-time ensures you don’t miss valuable targets.
4. Detecting Depth Analysis
The depth at which a target is detected provides critical information for planning your approach to recovery. Understanding depth readings enhances your overall efficiency in underwater metal detecting.
Tips for Detecting Depth Analysis
- Mapping Targets: Keep a mental map of detected targets and their corresponding depths. Over time, this mental database helps you anticipate the likely location of valuable items.
- Practice Precision: Hone your ability to pinpoint the exact location of targets based on depth readings. This precision is particularly valuable when dealing with closely packed targets or in areas with challenging conditions.
Underwater Metal Detector Maintenance and Care Tips
Effective maintenance is crucial for keeping your underwater metal detector in top-notch condition. Diligent care not only ensures its longevity but also enhances its performance during dives. Here’s why your detector demands your attention:
Post-Dive Cleaning
- Rinse the detector with fresh water after every dive to remove salt and debris.
- Ensure detailed cleaning, reaching into all crevices to eliminate any residue.
After each dive, take the time to thoroughly clean your underwater metal detector. This step is vital in preventing the accumulation of salt and debris, which could lead to corrosion and hinder the device’s functionality.
A meticulous post-dive cleaning routine will keep your detector in optimal condition for future underwater adventures.
Underwater Metal Detector Storage
- Store the detector in a secure, dry environment.
- Avoid extreme temperatures to maintain optimal functionality.
- Handle the detector with care during storage to prevent damage to internal components.
Proper storage is a crucial aspect of maintaining your underwater metal detector. Once cleaned, store it in a secure, dry environment.
Exposure to extreme temperatures can damage electronic components, so choose a cool, dry place to preserve its functionality.
Handle the detector with care during storage to prevent inadvertent damage that could impact its performance on future dives.
Preventing Corrosion and Damage
- Apply a protective coating to metal parts to prevent corrosion.
- Regularly inspect seals and connections for wear or damage.
- Promptly address any issues to prevent further damage.
Corrosion is a common issue for underwater metal detectors, given their exposure to saltwater. To mitigate this, apply a protective coating on metal parts. Additionally, inspect seals and connections regularly for any signs of wear or damage, addressing issues promptly.
Periodic Maintenance Routine
- Conduct periodic checks of all components.
- Test the functionality of the detector regularly.
- Stay informed about firmware updates and implement them as needed for improved performance.
Establish a periodic maintenance routine for your underwater metal detector. This includes a comprehensive check of all components, testing its functionality, and updating firmware if applicable.
Regular maintenance ensures that your detector remains a reliable and effective tool for your diving endeavors.
Underwater Metal Detecting and the Law
Underwater treasure hunting and metal detecting have potential legal implications that demand consideration. Compliance with relevant laws is necessary to avoid potential legal consequences.
Varied Legal Landscape: Laws governing underwater metal detecting vary greatly depending on the country or region. Proximity to coastlines, shipwrecks, war graves, and archaeological or environmental protection status can play a role in determining the legal status of these activities.
U.S. Legal Nuances: In the United States, specific regulations restrict diving for and retaining salvage within certain distances from coastlines (usually 3km), rendering such actions unlawful. National parks, including their underwater domains, commonly impose strict prohibitions on metal detecting.
Penalties for Unauthorized Treasure Hunting: Engaging in unauthorized treasure hunting, whether on land or underwater, may lead to legal penalties. Understanding and complying with specific laws in the region of activity is essential to navigate these potential consequences.
Archaeological Considerations: The use of metal detectors in archaeological contexts, both on land and underwater, typically demands official authorization. This precaution aims to prevent unauthorized excavation of historical sites and protect valuable cultural heritage.
In summary, prospective underwater treasure hunters and metal detector diving enthusiasts must conduct thorough research and adhere to the specific legal frameworks governing their chosen locations to ensure a lawful and respectful pursuit of their activities.
Why You Should Buy An Underwater Metal Detector
So, why should you dive into the world of underwater metal detecting? It’s more than just a hobby; it’s a specialized adventure for scuba divers. Using underwater metal detectors opens up a realm of possibilities—uncovering hidden treasures, exploring historical artifacts, and adding a thrilling dimension to your scuba diving experiences.
To make the most of this underwater pursuit, the careful selection of your metal detector is crucial. Consider your specific needs and objectives, the detector’s capabilities, and how well it compliments your diving skill and experience. The right choice ensures you dive with comfort, confidence, and competency, sustaining the overall safety and enjoyment of your dives.
As you embark on this unique journey, remember the importance of safe and responsible diving exploration. Respect the underwater environment, adhere to ethical guidelines, and revel in the thrill of discovery while preserving the beauty beneath the surface.
About The Author

Andy Davis is a RAID, PADI TecRec, ANDI, BSAC, and SSI-qualified independent technical diving instructor who specializes in teaching sidemount, trimix, and advanced wreck diving courses.
Currently residing in Subic Bay, Philippines; he has amassed more than 10,000 open-circuit and CCR dives over three decades of challenging diving across the globe.
Andy has published numerous diving magazine articles and designed advanced certification courses for several dive training agencies, He regularly tests and reviews new dive gear for scuba equipment manufacturers. Andy is currently writing a series of advanced diving books and creating a range of tech diving clothing and accessories.
Prior to becoming a professional technical diving educator in 2006, Andy was a commissioned officer in the Royal Air Force and has served in Iraq, Afghanistan, Belize, and Cyprus.
In 2023, Andy was named in the “Who’s Who of Sidemount” list by GUE InDepth Magazine.
Purchase my exclusive diving ebooks!
Originally posted 2023-10-03 13:25:00.















